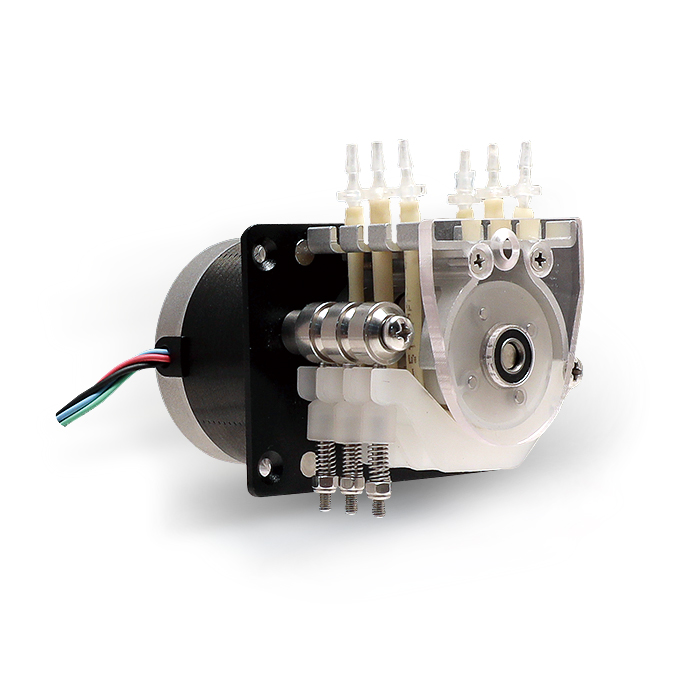
Roller pumps are widely utilized in various industries for their efficient and reliable performance in fluid transfer applications. These pumps offer a versatile solution for pumping fluids of different viscosities and are commonly used in agriculture, irrigation, chemical processing, and other industries. In this article, we will delve into the mechanics of roller pumps and explore how they work to facilitate fluid transfer.
Overview of Roller Pumps
- Pump Construction
Roller pumps consist of a pump housing, a rotating rotor assembly, and a series of rollers. The pump housing typically contains an inlet and an outlet port, as well as a cavity where the fluid is circulated during operation. - Roller Mechanism
The rotor assembly, driven by a power source such as an electric motor or an engine, rotates within the pump housing. The rotor features multiple lobes or lobes with grooves that house the rollers. The rollers are positioned to contact the inner surface of the flexible tube or impeller blades, creating the pumping action.
How Roller Pumps Work
- Priming and Startup
To initiate the pumping process, the pump housing is filled with the fluid to be transferred. The rotation of the rotor assembly causes the rollers to compress the flexible tube against the pump housing. The compression creates a seal and propels the fluid in a positive displacement manner, without the need for valves. - Fluid Transfer
As the rotor continues to rotate, the rollers sequentially move along the flexible tube, compressing it against the pump housing. This compression action propels the fluid through the tube in a peristaltic manner. The fluid is pushed towards the outlet port, creating a consistent flow. - Valveless Operation
Roller pumps operate without traditional valves found in other pump types. The compression of the flexible tube against the pump housing creates a positive displacement action, preventing backflow and enabling precise control over the fluid flow rate. - Reversibility
One of the advantages of roller pumps is their ability to operate bidirectionally. By reversing the rotation of the rotor assembly, the direction of fluid flow can be reversed. This feature allows for versatile applications, such as irrigation systems that require both forward and reverse fluid flow.
Key Advantages of Roller Pumps
- Versatility:Roller pumps are capable of handling a wide range of fluids, including liquids with varying viscosities, slurries, and abrasive fluids. This versatility makes them suitable for diverse applications in industries such as agriculture, chemical processing, and wastewater treatment.
- Self-Priming:Roller pumps are generally self-priming, meaning they can draw fluid from a lower elevation or suction source without the need for external priming mechanisms. This feature simplifies installation and improves operational convenience.
- High Flow Rates:Roller pumps can deliver high flow rates, making them suitable for applications requiring efficient transfer of large volumes of fluid. The positive displacement pumping action ensures consistent and controllable flow rates.
- Minimal Maintenance:Roller pumps have a relatively simple design with fewer moving parts compared to other pump types. This results in reduced maintenance requirements and lower associated costs.
Considerations and Limitations
- Viscosity Sensitivit
While roller pumps can handle a wide range of viscosities, their performance may be affected by extremely high-viscosity fluids. In such cases, selecting an appropriate pump size and configuration is crucial to ensure efficient operation. - Wear on Rollers and Tubes
The contact between the rollers and the flexible tube can cause wear over time, particularly when pumping abrasive fluids. Regular inspection and replacement of worn components are necessary to maintain pump performance and longevity.
Roller pumps provide a versatile and reliable solution for fluid transfer applications across various industries. By utilizing a rotor assembly with rollers to compress a flexible tube, these pumps achieve positive displacement and valveless operation. With their self-priming capability, roller pump high flow rates, and minimal maintenance requirements, roller pumps offer an efficient and cost-effective pumping solution for a wide range of fluid viscosities. Understanding the mechanics and advantages of roller pumps can guide the selection and implementation of these pumps in diverse fluid transfer applications